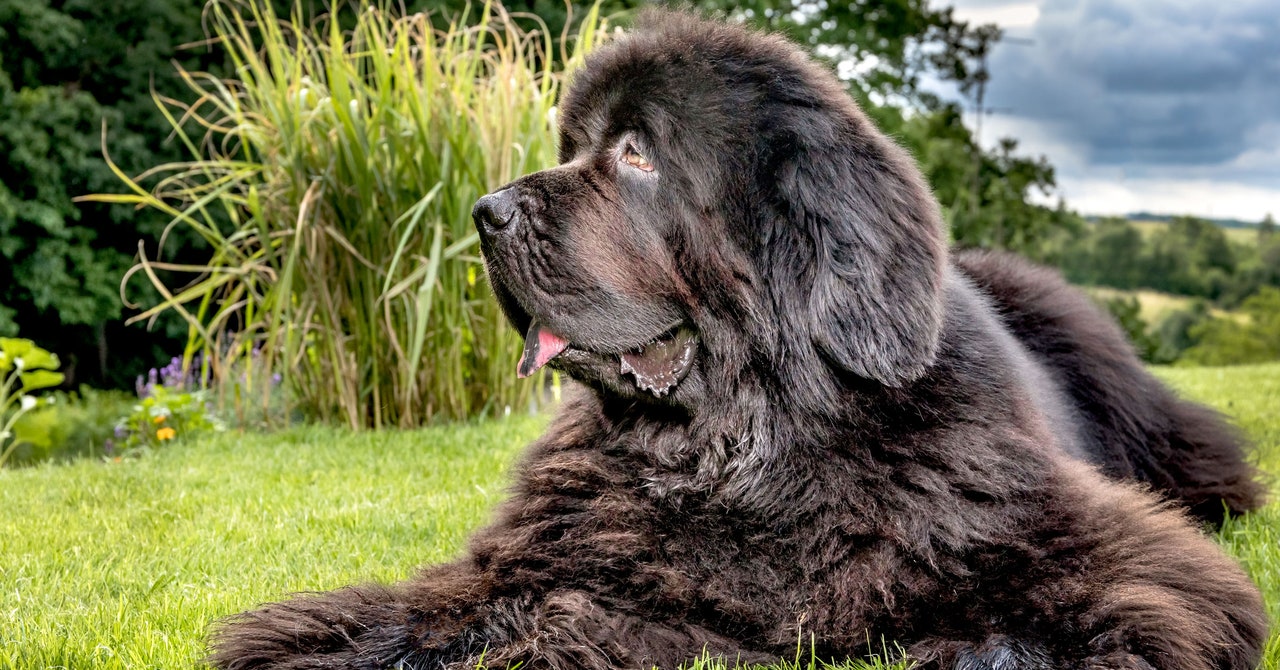
 “Big dog owners want more time with their dogs,” says Loyal CEO Celine Halioua. “It’s really heartbreaking to people that they don’t live that long.” She argues that the wide variety in dog sizes isn’t natural, but a result of selective breeding by humans to create dogs with certain physical traits or that can perform specific tasks. On average, mixed-breed dogs live longer than their purebred counterparts.
“Big dog owners want more time with their dogs,” says Loyal CEO Celine Halioua. “It’s really heartbreaking to people that they don’t live that long.” She argues that the wide variety in dog sizes isn’t natural, but a result of selective breeding by humans to create dogs with certain physical traits or that can perform specific tasks. On average, mixed-breed dogs live longer than their purebred counterparts.
So far, the FDA has not approved any drugs to expand the lifespan of animals—or humans, for that matter. “This is completely novel,” says Linda Rhodes, former CEO of pet biotech company Aratana Therapeutics and a consultant for Loyal. It’s difficult to study life-extension drugs in people, she says, because humans live relatively longer lives than other species. But starting with dogs—and the breeds with the shortest lives—could yield important clues. “The implication for other species, including humans, is pretty profound,” she says.
Loyal’s experimental drug is an injection designed to be given every three to six months by a veterinarian. The drug is meant to lower levels of a hormone called IGF-1, which is involved in growth and metabolism and has been linked to dog size. Large dogs have a genetic variant that leads to high levels of IGF-1 and small dogs have a different variant that results in lower levels.
Inhibiting this hormone has been shown to increase lifespan in worms, flies, and rodents. In humans, both very high and very low levels increase mortality risk, while a midrange is associated with the lowest mortality.
In early studies, Loyal dosed 130 research dogs with its investigational drug. Halioua says the company has shown that it can reduce IGF-1 levels in large dogs to those seen in medium-size dogs. Two dogs had loose stools for a day or two after receiving the injection, but beyond that, Halioua says, no major side effects have been observed.
Lire l’article complet sur : www.wired.com



Leave A Comment