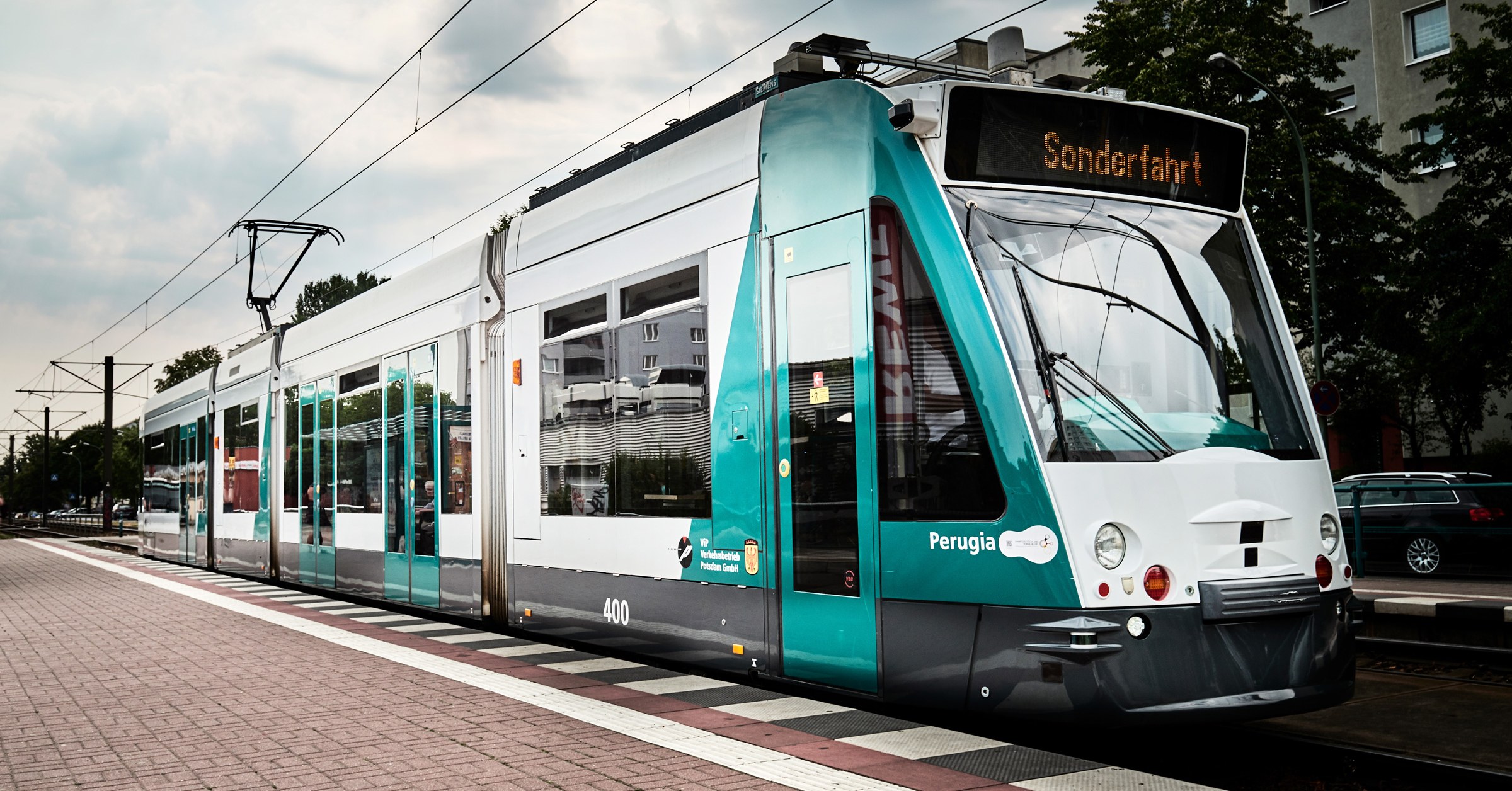
In the past year of trials, its (passenger-free) carriages have puttered through Potsdam more than 450 times. They use lidars, radars, cameras, and machine-learning software to interact with cars, pedestrians, and other denizens of the urban world on a 4-mile stretch of the existing network—chosen to be not too crazy busy, but not too easy either.
The trial is giving Siemens a chance to experiment in a way that isn’t easy with free-range cars and learn lessons that should aid the development of driver assistance and autonomous features for both road and rail vehicles. The promise of autonomous trams, trolleys, and streetcars is the same as for cars: Swap human drivers for computers that pay perfect attention, lack blind spots, and react faster than the human nervous system, and you improve safety. For now, though, the gains are just theoretical.
“The complexity is certainly a little lower,” says Christoph Klaes, who leads Siemens Mobility’s light-rail vehicle section. There’s no worrying about spotting faded lane lines or the exact angle to take through a turn. At its most basic, it just needs to think about velocity: when to stop, when to go, and how fast. That’s more complicated than it sounds, depending on grade, passenger loadings, and braking profiles. Stopping a big heavy vehicle without sending everyone on board tumbling takes skill, particularly uphill.
Sourced through Scoop.it from: www.wired.com






Leave A Comment